How Hiv Infects the Body
However HIV hides inside these cells tricking the body so that the immune. If the bodys immune system is strong lymphocytes manage to contain the bacteria and the infection does not spread.
AIDS is a set of symptoms and illnesses that develop at the final stage of HIV infection.
. 16 A person cannot get HIV from hugging or touching someone with HIVAIDS. HIV differs from HTLV in that the latter is a deltaretrovirus. Web Although HIVAIDS infects rich and poor alike it is most prominent in areas of poverty and where traditional social and family structures have been negatively impacted by economic and social practices that were established during the colonial era.
Web HIV is a retrovirus that primarily infects components of the human immune system such as CD4 T cells macrophages and dendritic cells. Web This virus infects the bodys immune cells called CD4 cells T cells which are needed to fight infections. Web HIV infects our immune system.
Because HIV works backward to insert its instructions into your DNA it is called a retrovirus. Acquired immune deficiency syndrome AIDS is the final stage of an HIV infection when the body is unable. Web How HIV Infects.
Web While there is no cure for HIV infection it can be treated using antiretroviral drugs which work by stopping the replication of the virus. HIV is a virus that can get into our bodies and start to make us sick over a period of time. That virus is known as simian immunodeficiency virus SIV and it was once widely thought to be harmless in chimpanzees.
Web HIV is thought to have originally mutated from a virus that infects chimpanzees called simian immunodeficiency virus. While some may consider the current treatments ART or antiretroviral treatment as a functional cure ideally a functional cure would suppress the virus without the need to take drugs for. It directly and indirectly destroys CD4 T cells.
Lentiviruses share many morphological and biological characteristics. When HIV has severely weakened your immune system it can lead to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome AIDS. Or by bug bites.
Web HIV is a virus that attacks and weakens the bodys immune system. They may look and feel healthy but without treatment HIV will slowly damage their body and they can pass HIV to others. ART can reduce the level of virus to such low levels in the body that the immune system will function normally and a person living with HIV can enjoy good health provided they adhere to treatment and the.
However in 2009 a team of researchers investigating. Web HIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus. However HIV and AIDS are very different.
While both are characterized by reverse transcription lentiviruses aggressively replicate while deltaretroviruses have minimal active replication once an infection has been established. HIV can become AIDS if it is not treated. But treatment means you can stay healthy and live a long life without getting AIDS.
This is the part of our body that stops us getting sick. Many species of mammals are. Web Reactivation is more likely to happen if the immune system is weakened such as with HIV infection or malnutrition.
Web HIV infects vital cells in the human immune system such as helper T cells specifically CD4 T cells macrophages and dendritic cells. As the virus weakens your natural defenses you might notice signs all over your body. HIV infects a type of white blood cell in our immune system called a T-helper cell also called a CD4 cell.
If you have HIV get treated. HIV infects humans and weakens the immune system compromising the bodys ability to fight off bacteria viruses and other agents that cause disease. HIV invades various immune cells eg CD4 T cells and monocytes resulting in a decline in CD4 T cell numbers below the critical level and loss of cell-mediated immunity therefore the body becomes.
HIV infection leads to low levels of CD4 T cells through a number of mechanisms including pyroptosis of abortively infected T cells apoptosis of uninfected bystander cells direct viral killing of infected cells and killing of. If not treated HIV infects and destroys CD4. Web HIV damages a persons body by destroying specific blood cells called CD4T cells which are vital in helping the body fight the disease.
Web HIV attacks your immune system making it harder for you to fight off things that can make you sick. Indeed the countries in Southern and Eastern Africa that have been most impacted by the HIVAIDS pandemics. Web A functional cure can reduce HIV in the body to levels that it cant be detected or make someone sick but it does not completely get rid of the virus from a body.
However a lentivirus that is genetically similar to HIV has been found in chimpanzees and gorillas in western equatorial Africa. Web Most people with HIV show few symptoms for years after infection. Research has indicated that the virus probably mutated into HIV which is a version that could infect humans as far back as the late 1800s when the chimpanzees were hunted for meat.
Web HIV and AIDS are different but connected. HIV lowers the number of these T cells in the immune system making it harder for the body to fight off infections and disease. Web Human immunodeficiency virus HIV a member of the retrovirus family is the causative agent of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome AIDS.
Web Details of the origin of HIV remain unclear. In summary there are three ways in which the body reacts to an infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. HIV spreads through contact with.
These cells keep us healthy by fighting off infections and diseases. Using public bathrooms or swimming pools. Web HIV is spread through body fluids including blood semen vaginal fluids anal mucus and breastmilk and from mother to child.
Sharing cups utensils or telephones with someone who has HIVAIDS. Web HIV is transmitted from an infected person by body fluids such as blood semen breast milk rectal fluids vaginal fluids or other blood-containing secretions. HIV transmission can be prevented by.
Web The terms HIV and AIDS are so closely associated that many people mistakenly consider them synonymous. HIV infects and destroys cells of your immune system making it hard to fight off other diseases. Protect yourself and others.
HIV cannot be spread through saliva or kissing hugging or shaking hands toilet seats insect bites sharing cutlery or crockery or by eating food prepared by a someone who is HIV-positive. Therefore individuals living with HIV are more susceptible to other diseases and infections. Know your statusget tested regularly for HIV.
In order for HIV to infect other cells in the body. Transmission occurs when these fluids come in contact with the various mucous membranes of the body through cutsopenings of the skin or directly injected into the. HIV is a member of the genus Lentivirus part of the family Retroviridae.

Frontiers Insights Into Persistent Hiv 1 Infection And Functional Cure Novel Capabilities And Strategies
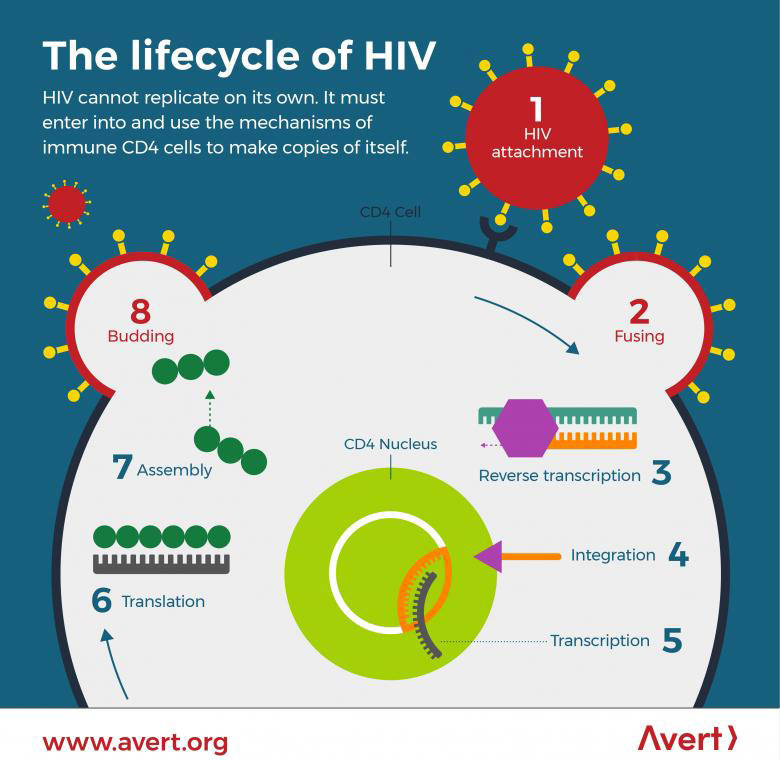
The Hiv Lifecycle How Hiv Enters Our Body And Reproduces Curious Chaser

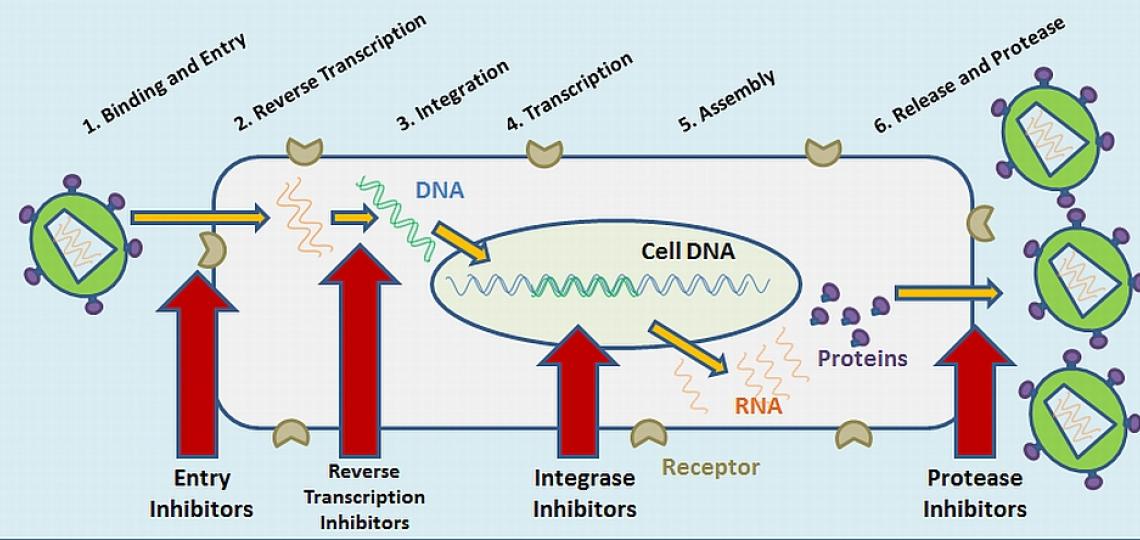

Comments
Post a Comment